The emotional impact of music
Music has the ability to express and evoke emotions that listeners can recognize and experience within themselves. Previous studies indicate that the primary reason for intentional music listening is often the emotional impact it provides. Whether it’s to enhance, reduce, or alter one’s mood, music holds the power to elicit emotions in roughly half of listening episodes, with positive emotions prevailing.
The strongest emotions are reported when music receives focused attention and when it is listened to alone. However, individuals sometimes find it challenging to differentiate between the emotions they genuinely felt while listening to music and those they perceive as inherent to the composition itself.
Which emotions does music induce?
The fact that music is able to evoke emotions is something that everyone has probably felt at some time. In research, there are three main approaches to the question of what kind of emotions are involved, whereby in our research we focus primarily on the latter.
- The dimensional approach represents emotions on the basis of the expression of several continuums, above all on the basis of the dimensions valence (positivity/negativity) and arousal (strength or intensity of the emotion).
- Discrete emotion models apply basic emotions such as joy, sadness, anger or fear to the measurement of music-induced emotions.
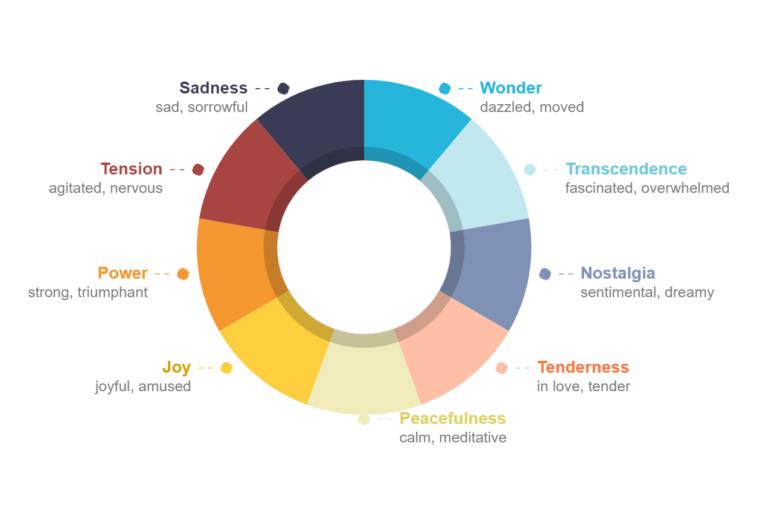
- Domain-specific approaches take into account the special character of aesthetic emotions and define music-specific emotion terms. One example is the GEMS, with 45 emotion terms, 9 dimensions and the three superordinate factors Sublimity, Vitality and Unease.
Factors influencing music induced emotions
Despite the general consensus among music listeners regarding the intended emotional expression of a piece of music, there exist variations among individuals in terms of the intensity and differentiation of their emotional responses to music.
These differences can primarily be attributed to four factors that influence the emotional impact of musical compositions: the musical structure, the performance, the personal characteristics of the listener, and the context in which the music is experienced.
In our research, we take a closer look at these four factors and their interactions and base our studies on the Induction Rule Model (Scherer & Zentner, 2001).